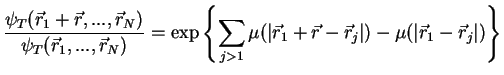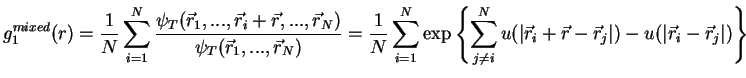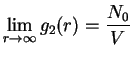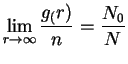


Next: One body density matrix
Up: Measured quantities
Previous: Static structure factor
Contents
The one body density matrix (OBDM) 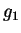 of a homogeneous system described by the
many body wave function
of a homogeneous system described by the
many body wave function
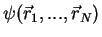 according to (1.18) is equal
to
according to (1.18) is equal
to
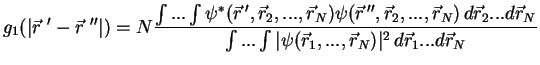 |
|
|
(2.139) |
Since in DMC calculation does not sample directly the ground-state probability
distribution 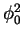 , but instead the mixed probability
, but instead the mixed probability 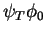 (2.12)
one obtains the mixed one-body density matrix as the output
(2.12)
one obtains the mixed one-body density matrix as the output
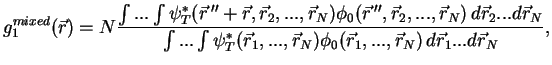 |
|
|
(2.140) |
This formula can be rewritten in a way convenient for the Monte Carlo sampling:
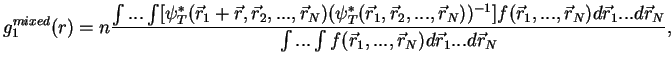 |
|
|
(2.141) |
where we have used the asymptotic formula (2.19) and have taken into
account that in a homogeneous system 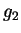 depends only on the module of the
relative distance between two particles. If the trial wave function is chosen as a
product of pair functions (2.37) then using the notation (2.38)
depends only on the module of the
relative distance between two particles. If the trial wave function is chosen as a
product of pair functions (2.37) then using the notation (2.38)
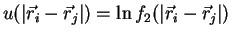 ) and
) and 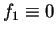 one has
one has
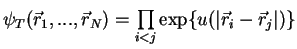 . Then the ratio of the trial wave function
appearing in (2.141) becomes
. Then the ratio of the trial wave function
appearing in (2.141) becomes
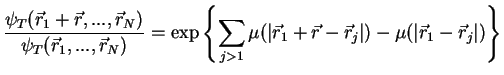 |
|
|
(2.142) |
In order to gain better statistics it is convenient to average over all possible
pairs of particles
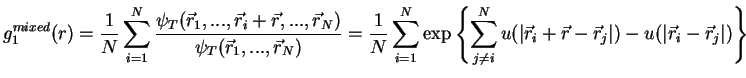 |
|
|
(2.143) |
The asymptotic limit of the OBDM gives the condensate density
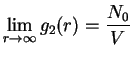 |
|
|
(2.144) |
and the condensate fraction is obtained by the calculating the asymptotic ratio
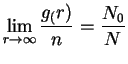 |
|
|
(2.145) |



Next: One body density matrix
Up: Measured quantities
Previous: Static structure factor
Contents
G.E. Astrakharchik
15-th of December 2004
![]() of a homogeneous system described by the
many body wave function
of a homogeneous system described by the
many body wave function
![]() according to (1.18) is equal
to
according to (1.18) is equal
to
![]() , but instead the mixed probability
, but instead the mixed probability ![]() (2.12)
one obtains the mixed one-body density matrix as the output
(2.12)
one obtains the mixed one-body density matrix as the output