In terms of the field operator (1.1) the momentum distribution ![]() is given as
is given as
Substitution of (1.24) into (1.23) gives following expression for
the momentum distribution
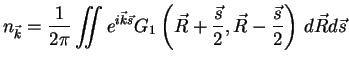 |
(1.25) |
Note, that the dependence on ![]() enters through the relative distance, so the center
of the mass motion can be integrated out independently of
enters through the relative distance, so the center
of the mass motion can be integrated out independently of ![]() . This procedure is
used in the DMC (see Sec.2.7). In the homogeneous system one has
. This procedure is
used in the DMC (see Sec.2.7). In the homogeneous system one has
At zero temperature the dynamic structure factor ![]() is related to the
is related to the
![]() -component of the density operator
-component of the density operator
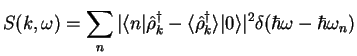 |
(1.28) |
It characterizes the scattering cross-section of inelastic reactions where the
scattering probe transfers momentum ![]() and energy
and energy ![]() to the
system. By integrating out the
to the
system. By integrating out the ![]() dependence we obtain the static structure
factor
dependence we obtain the static structure
factor
This expression is used in QMC calculations (refer to Sec. 2.7.2). Another
useful representation can be obtained from Eqs. (1.10,1.27) and
commutation relations for the field operator ![]() . It relates the static
structure factor to the two-body density matrix
. It relates the static
structure factor to the two-body density matrix
In a homogeneous system the two-body density matrix depends only on the relative
distance ![]() and the static structure factor
and the static structure factor ![]() is directly related to
the pair distribution function (1.12)
is directly related to
the pair distribution function (1.12)